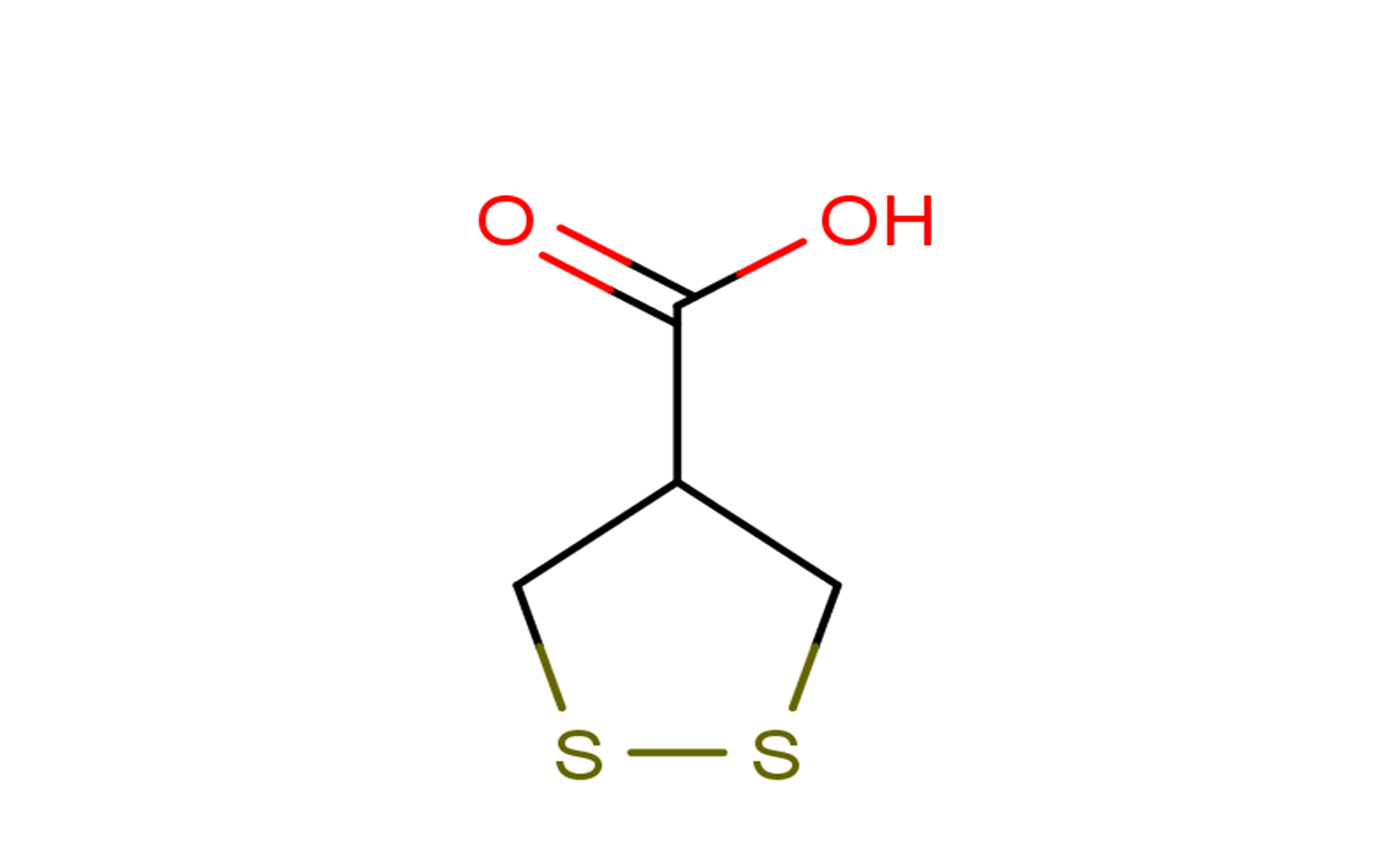
Asparagusic acid
CAS No. 2224-02-4
Asparagusic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M24007 CAS No. 2224-02-4
Asparagusic acid is unique to asparagus. It is responsible for the odorous urine excreted after eating asparagus. Its derivatives ihydroasparagusic acid have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 96 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 161 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 239 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 354 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 831 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAsparagusic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAsparagusic acid is unique to asparagus. It is responsible for the odorous urine excreted after eating asparagus. Its derivatives ihydroasparagusic acid have an anti-inflammatory effect.
-
DescriptionAsparagusic acid is unique to asparagus. It is responsible for the odorous urine excreted after eating asparagus. Its derivatives ihydroasparagusic acid have an anti-inflammatory effect.
-
In VitroAsparagusic acid is toxic to several plant parasitic nematodes and would be a major factor in resistance of asparagus.Asparagusic acid inhibits growth in lettuce and other seedlings at 6.67×10-7 M to 6.67×10-7 M.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2224-02-4
-
Formula Weight150.22
-
Molecular FormulaC4H6O2S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:46 mg/mL (306.22 mM)
-
SMILESC1C(CSS1)C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mitchell SC et al. Asparagusic acid. Phytochemistry. 2014 Jan;97:5-10.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Bisoxatin
Bisoxatin (LA 271A) is an oral laxative that can be used to study contact laxatives for chronic constipation.
-
Methyl 3-methoxyacry...
Methyl 3-methoxyacrylate is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Justicidin A
Justicidin A is a type of bioactive chemical from Justica procumbens.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


